Important SEO Considerations During a Website Redesign

Website Redesign: SEO Checklist
Launching a re-designed website is always a hectic time for site owners. One often overlooked but crucial aspect of a website redesign is an SEO migration plan. A website redesign can damage search visibility and cause a loss in organic traffic to your website if pre-emptive steps are not taken from the very start of the redesign process. Here at Arekibo, we recently held a workshop in which we presented a 7 step checklist to avoid losing organic search engine rankings when launching a redesigned website. Read the 7 steps below:
Skip To:
- Carry Out An SEO Audit
- Maintain Identified Optimised Content
- Carry Out An Inbound Link Analysis
- Implement 301 Redirects
- Design An Engaging Custom 404 Page
- Optimise Your Site Structure For SEO
- Re-Submit Sitemaps To Google Search Console & Bing Webmaster Tools
1. Carry Out An SEO Audit
The very first step in the process should be an SEO Audit of your current website. If you understand what works well and what doesn’t in terms of SEO on your current website, then you will be able to determine what should be migrated as-is and what can be left behind. Some factors to review at this stage include:
- Top landing pages
- Top organic landing pages
- Current search rankings for key search terms
- Missing / duplicate page titles
- Missing / duplicate H1 tags
- Missing / duplicate meta descriptions
- Meta descriptions over 923 pixels
- Image alt text
- XML sitemap
- Canonical tags
- Broken links
- Duplicate Content
- URL Structure
- robots.txt file
 Click to enlarge
Click to enlarge
Once you have reviewed and rated these key SEO factors, you can use this knowledge to construct a road map of what needs to be carried over and what needs to be optimised during the website redesign.
2. Maintain Identified Optimised Content
Very often, when a website is redesigned, the copy of the website also gets a refresh as webmasters / marketing departments / other stakeholders view this as a perfect time to remove outdated content, align content with up to date brand guidelines, focus content on more conversions, etc.
However, you should bear in mind that changing the copy on a page causes Google to re-evaluate the relevancy of that page for the targeted topic. If a large amount of changes are made to the copy e.g. high performing and relevant keywords are removed from key areas (title tag, header tags, body copy, alt text) then the relevancy score may drop leading to a drop in organic rankings and traffic.
It’s a delicate balance between refreshing old stale content and maintaining SEO rankings. Again, as a rule of thumb, you should keep what works and optimise what doesn’t. In other words, identify what search terms drive the most traffic to your top performing organic pages (which you will have identified in your SEO audit) and ensure that you do not remove content relevant to these terms.
One way of identifying top performing search terms is via the Search Console Report within Google Analytics. Log into Google Analytics, click ‘Acquisition’, then ‘Landing Pages’ and then view the top search queries for each of your top landing pages.
3. Carry Out An Inbound Link Analysis
“I can tell you what they are. It is content and links pointing to your site.”
That is the response of Andrey Lipattsev, a Search Quality Senior Strategist at Google, when asked what the first two Google search ranking signals are during a Google Q&A in March of this year. It’s debatable whether this constitutes as an official Google announcement or not, but what it does make very clear is that inbound links remain a critical factor for SEO.
Inbound links help to develop authority for your pages in search, especially inbound links from websites with high domain authority. So obviously, if your URLs are going to be changing as part of a website redesign, ideally, links that point to your digital content will need to be updated too.
There are a number of tools available online to help you to identify inbound links to your site. One such tool is MOZ Open Site Explorer, which will provide you with a complete list of inbound links to your website, where they come from, where they point to, whether they are considered “spammy” and the domain authority of the linking website.
Ideally, you should contact the webmaster hosting each link pointing to your site and request for them to update the URL (especially for those links from sites with high domain authority). If this is not feasible (because of the number of links, unreachable webmaster, etc.) you can preserve the majority of your “link juice” by establishing 301 redirects that point old URLs to new ones. Which brings us on to our next step…
4. Implement 301 Redirects
What Are Redirects And Why Do They Matter?
A redirect, put simply is a way to send users to a different URL from the one they originally requested. A redirect strategy is one of the most important SEO considerations when redesigning a website for a couple of reasons. Firstly, a redirect will send users to the new improved page instead of an Error 404 page when they type in an outdated URL. Secondly, a 301 Redirect will also tell search engines to pass the search value from the old page to the new page. There are a number of different types of redirects, but for this reason, 301 redirects should always be used.
A redirect strategy simply involves creating a list of all URLs on your old website, creating a list of all URLs on your new website and mapping old pages to the most relevant new pages.
It is critical that for your best performing pages on your old site (in terms of SEO), you should have an equivalent page on the new site with very similar content to which you can redirect traffic.
If a page is being eliminated or if there is no direct equivalent page on the new site, find the most relevant page on the new site for a 301 redirect – this will often be a main category page.
When 301 redirects are not planned and implemented, Google will reset the value on the new pages that were created (the old pages will 404 and drop out of the rankings), and in many cases, this will result in a loss in rankings and traffic.
 Click to enlarge.
Click to enlarge.
Step-By-Step Redirect Strategy
Step 1. Crawl your “Old” site
The first step in the process is to crawl your old website for a full list of URLs. There are a number of tools that will do this for you, one of which is Screaming Frog SEO Spider which is available to download for free. Simply download the tool, type in your website URL and hit ‘Start’.
This will compile a list of all URLs on your current site which you can export to Excel. Make sure to mark priority pages that you have identified in your SEO Audit (top organic landing pages) and your Inbound Link Analysis (those with the highest number of authoritative inbound links).
Step 2. Compile a list of URLs on your “New” site
Next you will want to compile a list of all planned URLs on your new website. There are a number of different ways to do this. You can use a free crawling tool like Screaming Frog again. Or depending on your CMS, there are also a number of alternative means of producing this list which are available as standard or as plugins.
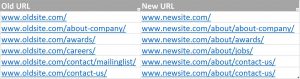
Step 3. Mapping URLs
Manually map each page on the old site with a corresponding page on the new site.
 Click to enlarge
Click to enlarge
Step 4. Implement your redirects
Now that you’ve mapped out all your redirects, it’s important that they are implemented as soon as the new site goes live. Otherwise users attempting to access pages via old URLs will be met with Error 404 pages. There are a number of means of implementing redirects, but we would recommend that ideally, they should be implemented by whoever is hosting your site at a server level.
Step 5. Monitor, Monitor, Monitor
In the hours, days and weeks after your redesigned website goes live, keep an eye on Google Search Console for crawl errors. If any 301 redirects have been overlooked or implemented incorrectly, they will be flagged here and you can get your development team / hosting provider to re-implement them.
5. Design An Engaging Custom 404 Page
As we’ve mentioned, there is a risk that some 301 redirects may be overlooked or implemented incorrectly. The result of this is an increased likelihood of users being presented with an Error 404 page. To avoid high bounce rates and ensure a good user experience where the user is quickly and intuitively able to find the content they are looking for, customised 404 pages are key.
You should make sure that the 404 page drives users to other relevant pages on the site, rather than to the ‘back’ button.
The custom 404 page should:
- Tell the user that the page cannot be found
- Use the same look and feel as the rest of your site
- Include links to popular content and the ‘home’ page
- Include a search box so that the user can search for the content they require
 Click to enlarge
Click to enlarge
6. Optimise Your Site Structure For SEO
The best time to develop a strong site structure is before you create your site in the first place. Site structure should be the product of collaborative thinking amongst stakeholders, user led design and logical organisation. If your original site structure is not optimal, a website redesign is the perfect opportunity to reorganise some navigational elements to improve structural SEO.
A good site structure:
- Means great user experience
- Provides your site with sitelinks in SERPs
- Means easier crawling for search engines
All of these factors contribute to great SEO.
Furthermore, site structure has a big impact on how SEO value is passed around your website. Google passes SEO value from one page to the next through internal links. Depending on where the pages are located in the hierarchy of the site, they will receive more or less of this value. So pages that are linked closer to the most important pages on your site in terms of SEO (e.g. Home page and Category pages) will receive more SEO value themselves.
Five Steps to Creating a Good Site Structure
Step 1. Plan out a hierarchy before you develop your site
Your hierarchy should be logical, should have between 2-7 main categories and should have evenly balanced subcategories
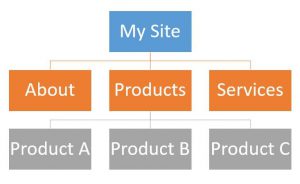
Step 2. Create a URL structure that follows your navigation hierarchy
So for example, if your hierarchy looks like this:
 Click to enlarge
The URL structure for the Product A page would look like this:
Click to enlarge
The URL structure for the Product A page would look like this:
www.mysite.com/products/product-a
Step 3. Create your navigation in HTML or CSS (Not JS/Flash/etc.)
It’s best to keep the coding simple when creating your navigational features e.g. Menu Bars. Coding in JavaScript, Flash or Ajax may limit crawlers’ ability to navigate the site.
Step 4. Use shallow depth navigation structure
Shallow sites work better in terms of both user experience and SEO. Ensure that important pages are not buried too deep in your site.
Step 5. Develop a comprehensive internal linking structure
Internal links support your primary navigation in telling search engines what pages are important and how to get there. They also allow users to navigate to relevant content more easily, and from an SEO perspective, they help to spread SEO value around your website.
7. Re-Submit Sitemaps To Google Search Console & Bing Webmaster Tools
XML Sitemaps are a useful tool which essentially feed search engines data on the pages of a site they want crawled as well as the priority or hierarchy of site content. Sitemaps can be created quite easily (e.g. through your CMS or a plugin) and should be uploaded and submitted to Search Engines e.g. Google, Bing, Yahoo etc. when a site is initially launched and also when a site is redesigned.
When uploading your sitemap, you should ensure that the sitemap.xml file resides directly off the root folder with a relevant page naming convention i.e. /sitemap.xml.
After this, you will want to submit your sitemap to relevant search engines. For Google, you do this through Google Search Console. Simply navigate to ‘Crawl’ – ‘Sitemaps’ – ‘Add/Test Sitemap’.
 Click to enlarge
Click to enlarge
Conclusion
As you’ve probably figured, it’s unlikely in the short term that your new website will rank better for SEO than your old one. The primary objective should be to ensure that your redesigned website performs as well as your old site in the short term. In fact, you are likely to see rankings take an initial dip while the engines are picking up your 301s and assessing the new pages.
However, if you involve your SEO team from the very start of the redesign planning process and stick to the checklist above you will stand a great chance of minimising the initial effects of the redesign and improving your website’s SEO rankings in the longer term.
To recap:
- Know your current site – what works well, what doesn’t
- Know your backlink profile – where your inbound links come from
- Consider SEO from the start
- Implement 301 redirects (and 404 pages)
- Make it easy for Google (and other search engines) - to index and crawl your new site
If you’re planning a website redesign and would like any advice or assistance get in touch with Arekibo here.